Functions of cell membrane : Videos
Functions of cell membrane : Photo Gallery
Functions of cell membrane : Latest News, Information, Answers and Websites
What is the functions of the cell membrane?
Answer: The cell membrane is the boundary that seperates one cell from either its neighboring cells or its liquid environment. It holds the cellular contents together, determines the shape of the cell and is semi-permeable which means it allows some particles to cross it.
Category: Other - Health
Describe two primary functions of the cell membrane?
this is something is just that I cant figure out...! help me please.
Answer: The cell membrane is a very important structure which functions to allow certain substances to enter or leave the cell. It can "pump" other substance into the cell against the concentration gradient or pump other "wastes" etc. out of the cell. :)
Category: Biology
Plant Physiology - Cell Walls: Structure & Function
Feb 6, 2009 ... Cell Walls - Structure & Function. I. Functions of the cell wall: The cell wall serves a variety of purposes including: ...
What are two functions of a cell membrane
The two main functions of the cell membrane -to protect the cell's contents from its environment -to be a barrier that encloses the cell ...
What's the Nucleolus? « Sam Doctor Sam Doctor
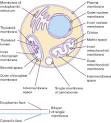
To start using the basics of a cell, let's consider the center with the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, here, we notice the nucleus with the cell. A nucleus is actually a membrane structure that carries the hereditary information of a cell and moderates the ... With this brief take lets delve further below and discover out what exactly is the nucleolus made of? What exactly is the structure and functions of cell nucleus… What may be the Nucleolus of a Cell? ...
Cell Nucleus Function « Sam Doctor Sam Doctor
Each and every part has specific functions that is widespread for eucaryotic plants and animals. The parts of a cell nucleus are:Nuclear Membrane: Also referred to as nuclear envelope, it encloses the contents with the ...
Besides being a boundary to the external environment what are some other functions of the cell membrane?
Answer: to act as a wrapper to keep the contents of the cytoplasm IN.
Category: Homework Help
What are the functions of the cell membrane?
Where are proteins found in the cell membrane?
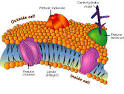
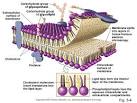
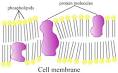
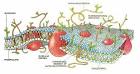
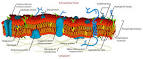
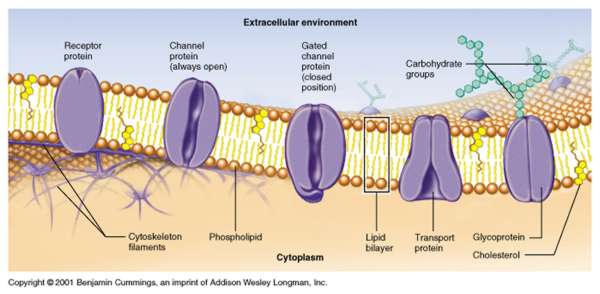
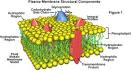
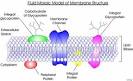
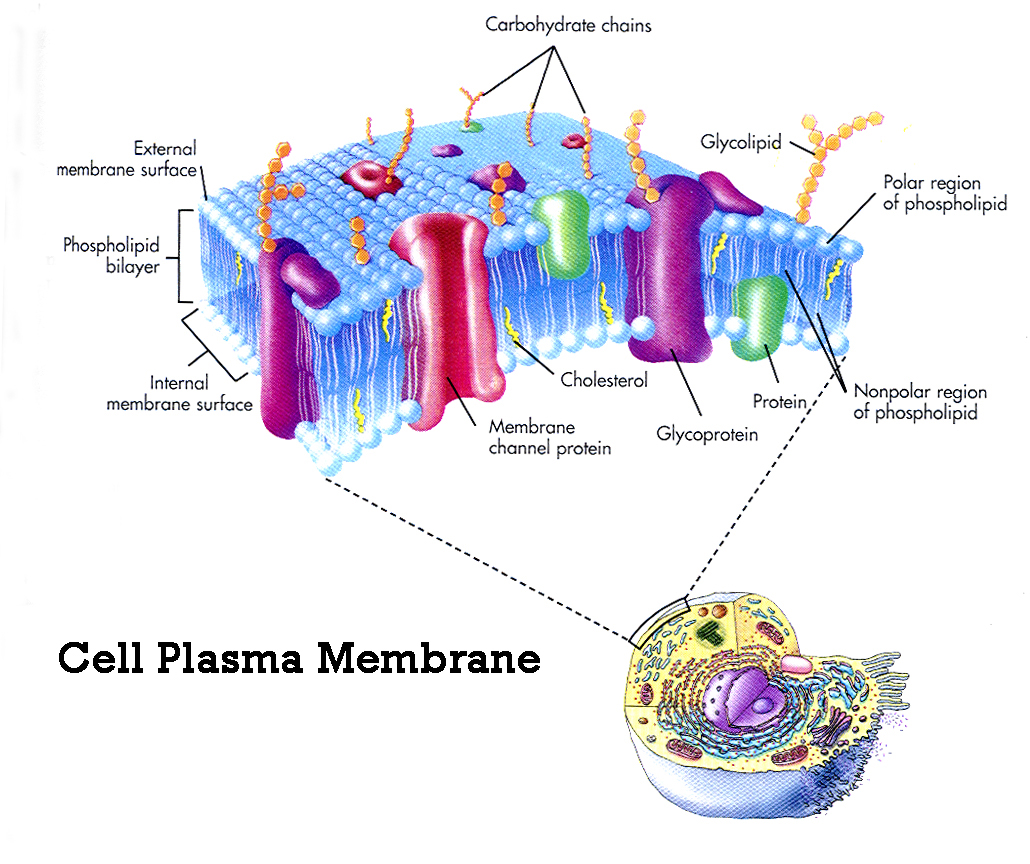
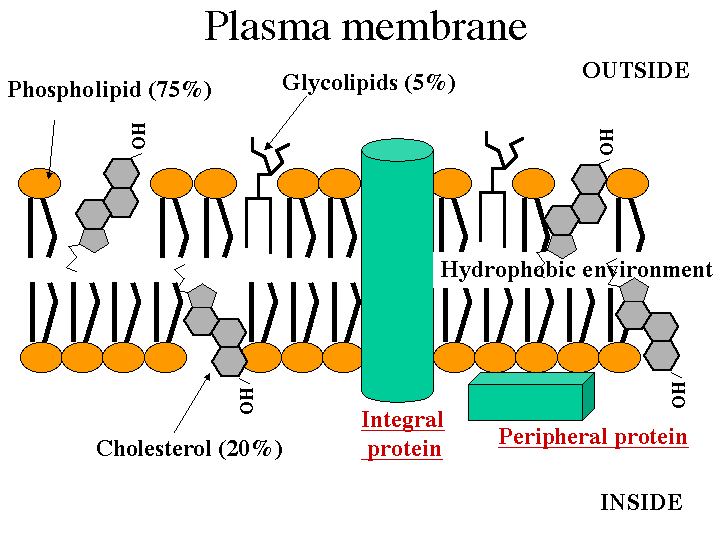
Answer: The plasma membrane is a dynamic structure. It is composed of 2 layers of lipid material with protein molecules located through out. The phospholipids move at a rate of 2um. /sec. while the proteins move at a much slower rate. The phospholipids have 2 definite ends, a hydrophilic (focusing to the outside and inside of the membrane) and a hydrophobic one (forming the center of the membrane). The proteins are of two types Integral (passing through the width of the membrane act as transport channels) and peripheral (act as recognition sites). These peripheral proteins contain carbohydrates to help in cell to cell recognition. These carbohydrates are called oligosaccharides. If they bind to proteins they become glycoproteins, if they bind to lipids, they become glycolipids. Cholesterol molecules are found in animal membranes to help add support to its structure. The majority of the phospholipids contain unsaturated fatty acids to keep it fluid.
Category: Biology
One of the functions of fat in the body is to provide fluidity of the cell membrane for proper cell function?
is this true?
Answer: Yes, example: cholestrol.
Category: Biology
Which material matches the function of the following cell organelles?
I have to make a project which is due tommorow! Please help me!
I need to know the materials found in our everyday world to match the following organelles and their functions:
-Cell Membrane
-Chromosomes
-Nucleolus
-Nuclear Envelope
-Vacuole
-Ribosomes
-Golgi Apparatus
-Lysosomes
-Mitochondria
-Rough ER
-Smooth ER
Answer: If your talking more relating them to the roles they would represent.....
Then:
Mitochondria-power house (produces energy)
Cell membrane- doors or guard (lets things in and out)
Golgi-postal service (package and transport)
Vacuole-water fountain or water bottle (water source)
Rough ER- like train on tracks or semis on highway (transport proteins)
Lysosome-either garbage men or army(clean up and destroy)
Ribosome-factory (assembly line for amino acids being put together into proteins)
Smooth ER-can also be highway but no semis
Nucleolus- either builder of factory or manager of assembly line (make ribosomes)
Nuclear envelope-guards to city center (controls what gets in and out of nucleus [control center])
Chromosomes-blueprints for the city
Hope this is what you need and its not too late
Category: Biology
Membrane Structure and Function - Cell Biology and Cytochemistry
Jul 10, 2001 ... Cellular membranes have diverse functions in the different regions and organelles of a cell. However, at the electron microscopic level, ...
Human Physiology - Cell structure and function
Osmosis = diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane (like a cell membrane) from an area of low solute ...
Functions of the Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is a very important structure which functions to allow certain substances to enter or leave the cell. It can "pump" other substance into ...
Short, simple definition for the functions of these animal cell terms?
Hey there. Can you guys give me a SUPER SHORT but good enough definition for these terms functions :
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough ER
Ribosomes
Golgi complex
Vacuoles
and Lysosomes
EXAMPLE: Mitochondria - Powerhouse of cell
thanks in advance!
Answer: Cell Membrane - selectively permeable barrier
Cytoplasm - jelly-like inside of the cell
Nucleus - control room
Nucleolus - operating desk in the control room
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum - Transport network that makes lipids
Rough ER - Transport network that makes proteins
Ribosomes - protein manufacturer
Golgi complex - final transporter and modifier of proteins
Vacuoles - digestive stomach for plant and fungal cells
and Lysosomes - digestive stomach for animal cells
Category: Biology
what are the functions of cell membrane?
Answer: The membrane of a cell functions to regulate the inflow of resources and outflow of waste, protects the internal machinery of the cell from damage, adheres to other cells or compounds and contains receptors that are involved in inter-cellular signalling and taxis.
Category: Biology
The Functions of the Cell membrane are necessary for the existence of life?
I have a 30 min essay to write on this topic. Now - 30 mins seems like nothing! Im torn between wanting to include major details and not knowing what to throw out of the essay to be able to cram in what is required.
What do you think a 30 min 1-1.5 side of paper essay would include?
Many thanks
Answer: The cell membrane (also called the plasma membrane, plasmalemma or "phospholipid bilayer") is a semipermeable lipid bilayer found in all cells.[1] It contains a wide variety of biological molecules, primarily proteins and lipids, which are involved in a vast array of cellular processes, and also serves as the attachment point for both the intracellular cytoskeleton and, if present, the cell wall.
Function
The cell membrane surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell and, in animal cells, physically separates the intracellular components from the extracellular environment, thereby serving a function similar to that of skin. In fungi, bacteria, and plants an additional cell wall forms the outermost boundary, however, the cell wall plays mostly a mechanical support role rather than a role as a selective boundary. The cell membrane also plays a role in anchoring the cytoskeleton to provide shape to the cell, and in attaching to the extracellular matrix to help group cells together in the formation of tissues.
The barrier is selectively permeable and able to regulate what enters and exits the cell, thus facilitating the transport of materials needed for survival. The movement of substances across the membrane can be either passive, occurring without the input of cellular energy, or active, requiring the cell to expend energy in moving it. The membrane also maintains the cell potential.
Specific proteins embedded in the cell membrane can act as molecular signals which allow cells to communicate with each other. Protein receptors are found ubiquitously and function to receive signals from both the environment and other cells. These signals are transduced into a form which the cell can use to directly effect a response. Other proteins on the surface of the cell membrane serve as "markers" which identify a cell to other cells. The interaction of these markers with their respective receptors forms the basis of cell-cell interaction in the immune system.
Structure
Lipid bilayer
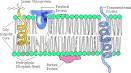
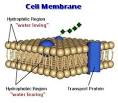
Diagram of the arrangement of amphipathic lipid molecules to form a lipid bilayer. The yellow polar head groups separate the grey hydrophobic tails from the aqueous cytosolic and extracellular environments.The cell membrane consists of a thin layer of amphipathic lipids which spontaneously arrange so that the hydrophobic "tail" regions are shielded from the surrounding polar fluid, causing the more hydrophilic "head" regions to associate with the cytosolic and extracellular faces of the resulting bilayer. This forms a continuous, spherical lipid bilayer containing the cellular components approximately 7 nm thick, barely discernible with a transmission electron microscope.[1]
The arrangement of hydrophilic and hydrophobic heads of the lipid bilayer prevents hydrophilic solutes from passively diffusing across the band of hydrophobic tail groups, allowing the cell to control the movement of these substances via transmembrane protein complexes such as pores and gates.
Flippases and Scramblases concentrate phosphatidyl serine, which carries a negative charge, on the inner membrane. Along with NANA, this creates an extra barrier to charged Moities moving through the membrane.
Integral membrane proteins
The cell membrane contains many integral membrane proteins which pepper the entire surface. These structures, which can be visualized by electron microscopy or fluorescence microscopy, can be found on the inside of the membrane, the outside, or through-and-through. They include synapses, desmosomes, clathrin-coated pits, caveolaes, and different structures involved in cell adhesion.
Membrane skeleton
The cytoskeleton is found underlying the cell membrane in the cytoplasm and provides a scaffolding for membrane proteins to anchor to, as well as forming organelles which extend from the cell. Anchoring proteins restricts them to a particular cell surface — for example, the apical surface of epithelial cells that line the vertebrate gut — and limits how far they may diffuse within the bilayer. The cytoskeleton is able to form appendage-like organelles, such as cilia, which are covered by the cell membrane and project from the surface of the cell. The apical surfaces of the aforementioned epithelial cells are dense with finger-like projections, called microvilli, which increase cell surface area and thereby increase the absorption rate of nutrients. The cell membrane acts as a protecting body.
Structure and the Fluid mosaic model
According to the fluid mosaic model of S. Jonathan Singer and Garth Nicolson, the biological membranes can be considered as a two-dimensional liquid where all lipid and protein molecules diffuse more or less freely[2]. This picture may be valid in the space scale of 10 nm. However, the plasma membranes contain different structures or domains that can be classified as (a) protein-protein complexes; (b) lipid rafts, (c) pickets and fences formed by the actin-based cytoskeleton; and (d) large stable structures, such as synapses or desmosomes.
The flud mosaic model can be seen when the membrane proteins of two cells (eg a human cell and a mouse cell) are tagged with different coloured fluorescent labels. When the two cells are fused, the two colours intermix, indicating that the proteins are free to move in the 2D plane.
Category: Biology
ARIIX MLM Watch Dog - ARIIX Products Contain an Ingredient Listed ...
Studies by the University of Texas Health Science Center and the East Carolina University School of Medicine reveal that these toxic excipients cause a rapid collapse of T-cell membrane function and cell death; ...
cell membrane functions: true or false?
free ribisomes differ from membrane-bound ribosomes in that free ribosomes specialize in synthesizing proteins for export (secretion) from the cell.
one function of integral proteins in the plasma membrane of cells is to form channels to allow passage of nonpolar solutes into the cell.
thanks for your help!
Answer: true and true.
From Wiki:
Free ribosomes
Free ribosomes are free to move about anywhere in the cytoplasm (within the cell membrane). Proteins that are formed from free ribosomes are used within the cell. Proteins containing disulfide bonds using cysteine amino acids cannot be produced outside of the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum.
[edit] Membrane-bound ribosomes
When certain proteins are synthesized by a ribosome they can become "membrane-bound". The newly produced polypeptide chains are inserted directly into the endoplasmic reticulum by the ribosome and are then transported to their destinations. Bound ribosomes usually produce proteins that are used within the cell membrane or are expelled from the cell via exocytosis.
Free and membrane-bound ribosomes differ only in their spatial distribution; they are identical in structure and function. Whether the ribosome exists in a free or membrane-bound state depends on the presence of a ER-targeting signal sequence on the protein being synthesized.
[
Category: Biology
Cell membrane - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Function. The cell membrane surrounds the protoplasm of a cell and, in animal cells, physically separates the intracellular ...
Nucleus Function in a Cell « Sam Doctor Sam Doctor
The nucleus function in a cell is attributed to its numerous components. The membrane with the cell nucleus is double layered along with the space in between the two layers is known as the perinuclear space. ...
Cell control to change cell function « Integrative Biology Blog
'The experiments provide further confirmation for the central role of ligand induced receptor dimerisation in cell signalling across the cell membrane,' says Joseph Schlessinger, professor of pharmacology from the school ...
Cellular Health & Omega 3 Fatty Acids
The fluid aspect of the cell is essential for the mobility and function of embedded protein receptors, diffusion of proteins and other molecules laterally across the membrane for signaling reactions, and proper separation of membranes ...
Cell Membrane Function | Berry Minder for Your Business Insurance
As the nature of the function of the cells differ, the functions of different parts of the cells too differ. Let us take a appear at the different parts of a cell, specifically, the cell membrane and cell membrane ...
What are the functions of cell membranes?
describe AT LEAST 3 separate functions.
Include a brief background on membrane structure to support your descriptions.
Use the following vocabulary: phospholipid bi-layer; fluid mosaic model; active and passive transport; diffusion and osmosis.
Thanks.
this is college level stuff here, just tryin to get some useful information..
Answer: 1. cell membrane gives the cell its shape as you see it under the microscope.that is the fluid mosaic model.
2.the cell membrane defines waht goes in and what is going out. it lets in water and nutrients and lets out waste materials.active and passive transport plus diffusion and osmosis apply here.
3.the phospholipid layer is strong and protects the organelles from shocks and pathogens.
you should note that the cell membrane of a plant and an animal have slightly different structures and therefore functions vary.
Category: Biology
What are 3 functions of cell membrane?
Answer: She wants something from your book, there are more than 3 functions of a cell membrane.
protection
transport (stuff needs to go in and out through the membrane)
provides anchoring sites
allows cell recognition
regulates fusion
motility (movement)
those are the ones i can think of ...there are problably more
Category: Biology
describing the functions of the cell membrane and the cell wall?
it would be of very help, its on an essay i need to write, and i cant seem to get a strong understanding of it..
Answer: cell wall and cell membrane serves as the shield of the cell in its outside environment in general..
I'll give you the outline of uses:
Cell Wall
-Found ONLY on plants, bacteria, fungi, algae, and archea
-Provides Rigidity for plants
-Maintaining the amount of water entering and leaving the cell (osmosis)
-Filters materials entering the cell (semi-permeable)
-Lies outside the cell membrane
~Cell Wall for plants
-It's major component is cellulose
-Compose of 3 layers
....= * The middle lamella, a layer rich in pectins. This outermost layer forming the interface between adjacent plant cells and glues them together.
* The primary cell wall, generally a thin, flexible and extensible layer formed while the cell is growing.
* The secondary cell wall, a thick layer formed inside the primary cell wall after the cell is fully grown. It is not found in all cell types. In some cells, such as found xylem, the secondary wall contains lignin, which strengthens and waterpoofs the wall.
~Cell Wall for algae
-major component is cellulose
~Cell Wall for bacterias (including archea)
-Made up of cellulose and chitin
For the cell membrane
-It is found on ALL cells
-Semi Permeable
-Control the fluids inside the cell (to prevent shrinkage or expansion)
-Some proteins allow cell to communicate on each other
(concrete example is when the cell becomes tissue-organ-organ system-human being)
Category: Biology
Cell Nucleus « Sam Doctor Sam Doctor
This membrane protects the DNA and other genetic material present inside the nucleus.The cell nucleus size is measured in microns or micrometers and is roughly 1.7 ?m.The main cell nucleus function is storing the ...
Cell Membrane Function
Jan 8, 2010 ... Cell Membrane Function. Cell membrane is the outer covering of a cell, ... Scroll down for information about cell membrane function. ...
Function of cell membrane - NEWTON, Ask a Scientist at Argonne ...
Many, many specific functions, but they can best be summarized this way: the cell membrane forms a barrier between the inside of the cell and the outside, ...
What are the five functions of the cell membrane?
Also, Describe the mechanisms of membrane transport.
Answer: Passive transport
Active transport
Pinocytosis
Phagocytosis
Cell recognition
Category: Biology
How does the endoplasmic reticulum and cell membrane work together to preform the life functions of the cell?
AP Bio.
ive looked evrywhere :(
Answer: Rough endoplasmic reticulum is used to manufacture proteins that will subsequently end being embedded in the cell membrane (or anchored to it) or be released outside of the cell. Meanwhile the smooth ER adds phospholipids to the cell membrane via exocytosis so they work together to maintain a normal cell size. Hope this helps!
Category: Biology
Cell membrane functions as a selective barrier? 10 PTS?
The ____ component of the cell membrane functions as a selective barrier, while the ____ component has specific functions such as transport, recognizing other cells, and binding to other cells.
a. lipid; protein
b. protein; cholesterol
c. carbohydrate; protein
d. protein; lipid
e. lipid; carbohydrate
Answer: The answer is A
the phospholipid bilayer is a selective barrier and there are different proteing that are either internal external or throughout the layer to allow movement through the membrane.
Category: Biology